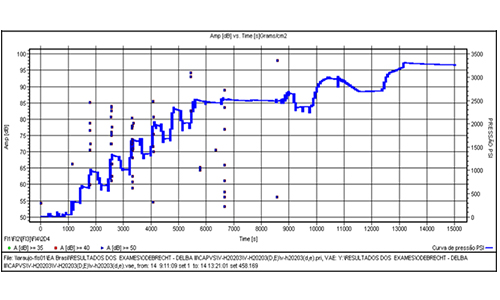
FRP
In composite materials, acoustic emission examination can detect damage such as: resin cracking, fiber detachment, fiber breakage, delamination and failure to “glue” assembled joints (for example connections, manholes, etc.). Faults in unstressed areas and faults that are structurally insignificant do not generate acoustic emission.
This practice is convenient for in-service inspection to determine structural integrity of in-service equipment with minimal process disruption.
Indications located by Acoustic Emission can be examined by other techniques such as visual examination, ultrasound, liquid penetrants, etc. and can be repaired and tested appropriately.
For FRP materials (fiberglass reinforced plastic) ASME V standards – article 11 and ASTM E 1067/1067M are used as a reference.
This practice is convenient for in-service inspection to determine structural integrity of in-service equipment with minimal process disruption.
Indications located by Acoustic Emission can be examined by other techniques such as visual examination, ultrasound, liquid penetrants, etc. and can be repaired and tested appropriately.
For FRP materials (fiberglass reinforced plastic) ASME V standards – article 11 and ASTM E 1067/1067M are used as a reference.